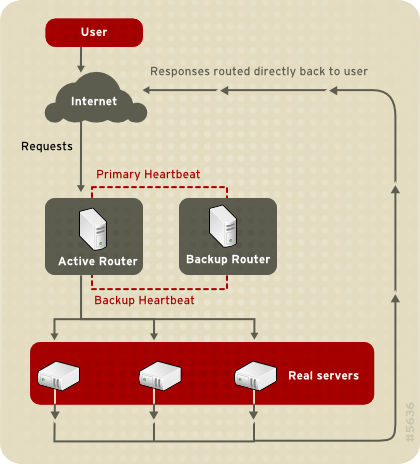
Building an LVS setup that uses direct routing provides increased performance benefits compared to other LVS networking topographies. Direct routing allows the real servers to process and route packets directly to a requesting user rather than passing all outgoing packets through the LVS router. Direct routing reduces the possibility of network performance issues by relegating the job of the LVS router to processing incoming packets only.
In the typical direct routing LVS setup, the LVS router receives incoming server requests through the virtual IP (VIP) and uses a scheduling algorithm to route the request to the real servers. The real server processes the request and sends the response directly to the client, bypassing the LVS routers. This method of routing allows for scalability in that real servers can be added without the added burden on the LVS router to route outgoing packets from the real server to the client, which can become a bottleneck under heavy network load.